Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are a serious health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. One crucial step in taking control of your sexual health is undergoing regular STD testing. The variety of available testing options can be overwhelming, but understanding your choices is key to making informed decisions about your well-being. In this article, we explore different STD testing methods and help you determine what might be right for you.
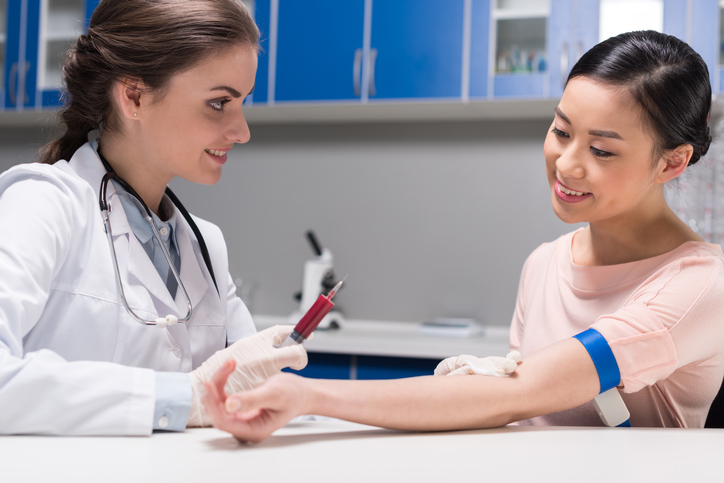
- Blood Tests:Blood tests are a common and effective method for detecting certain STDs. They involve drawing a small blood sample to check for the presence of antibodies or specific antigens that indicate an infection. Blood tests are commonly used for HIV, syphilis, and herpes (HSV).
- Suitable for: HIV, syphilis, herpes
- Advantages: High accuracy, can detect infections even if asymptomatic
- Considerations: Some STDs may not be detectable immediately after exposure; results may take a few days to a few weeks.
- Urine Tests:Urine tests are convenient and non-invasive, making them a popular choice for detecting certain STDs like chlamydia and gonorrhea. Individuals provide a urine sample, which is then analyzed for the presence of bacterial DNA or antigens.
- Suitable for: Chlamydia, gonorrhea
- Advantages: Non-invasive, easy sample collection
- Considerations: Accuracy can be affected by recent urination; may not detect infections in the throat or rectum.
- Swab Tests:Swab tests involve collecting samples from the genital, oral, or rectal areas using a cotton swab. These samples are then analyzed to detect the presence of pathogens. Swab tests are commonly used for STDs such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and herpes.
- Suitable for: Chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes
- Advantages: Direct sampling from affected areas, high accuracy
- Considerations: May be slightly uncomfortable, especially for those not accustomed to medical procedures.
- Rapid Tests:Rapid tests provide quick results within minutes, making them advantageous for immediate detection. They often involve a small blood sample or oral swab. Rapid tests are commonly used for HIV and, more recently, for syphilis and hepatitis.
- Suitable for: HIV, syphilis
- Advantages: Quick results, suitable for point-of-care testing
- Considerations: May have a slightly lower sensitivity compared to traditional laboratory tests.
- Home Testing Kits:Home testing kits are becoming increasingly popular, providing individuals with the convenience of testing in the privacy of their own homes. These kits typically involve collecting a sample (urine, blood, or swab) and sending it to a laboratory for analysis.
- Suitable for: Various STDs, depending on the kit
- Advantages: Privacy, convenience
- Considerations: Accuracy may vary; follow instructions carefully, and results may take a few days.
Choosing the Right Option:
The right STD testing method for you depends on various factors, including your preferences, the specific STDs you want to test for, and how soon after potential exposure you’re seeking testing. Consult with a healthcare professional to discuss your concerns, risk factors, and the most appropriate testing options based on your individual circumstances.
Conclusion:
Regular STD testing is a crucial aspect of maintaining your sexual health and preventing the spread of infections. With diverse testing methods available, individuals can choose the option that aligns with their needs, preferences, and the specific STDs they want to screen for. Being informed about your choices empowers you to take proactive steps in preserving your well-being and that of your sexual partners. If you have any concerns or questions, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from healthcare professionals who can provide personalized advice tailored to your situation.